Vertical farming rises as a viable and “groundbreaking” solution to the pressing issues of water scarcity and sustainable agriculture. By reimagining the way we grow crops, these creative minds are not just cultivating plants—they’re cultivating a sustainable future.
In vertical farming, every layer, system, and component is meticulously designed to optimize resource efficiency and maximize plant yields, changing the game in agricultural practices.
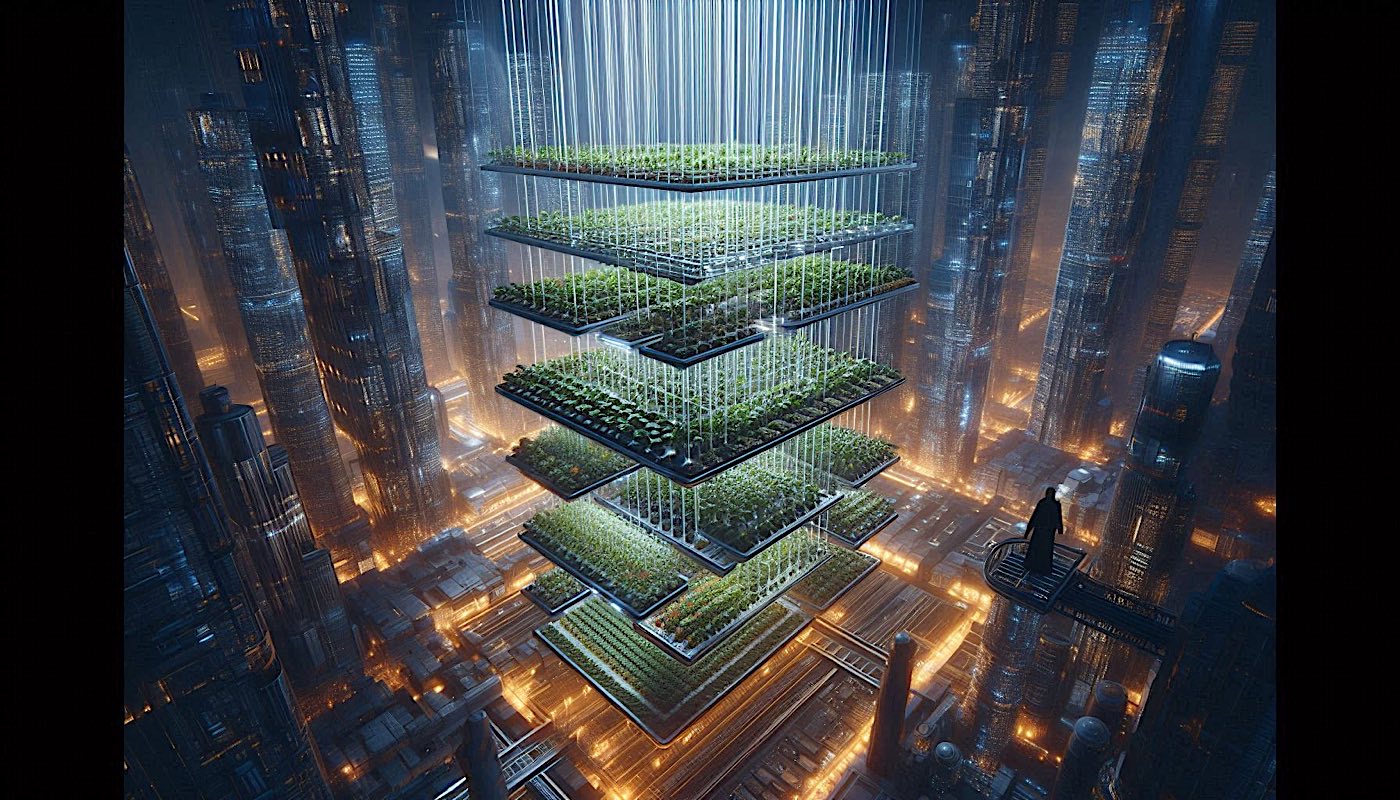

Vertical Agriculture relies on engineering precision and design innovation to achieve sustainability objectives. Here’s how designers and engineers are tackling the challenges:
- Creating highly efficient irrigation systems that drastically reduce water use.
- Designing controlled environments to boost crop yields with minimal energy.
- Integrating smart technologies for real-time monitoring and adjustments.
Quick Facts
- Vertical farming can reduce water usage by up to 95% compared to traditional farming methods.
- Vertical farms can produce crops year-round, independent of weather conditions.
- Vertical farming uses hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics systems to grow plants without soil.
- Vertical farming can significantly reduce the need for pesticides and herbicides.
- Urban vertical farms can reduce transportation emissions by growing food closer to consumers.
- Vertical farming supports biodiversity by allowing the cultivation of a wide variety of crops.

Vertical Farming: A Solution to Global Food Security
As urban areas continue to grow, the demand for fresh, locally produced food increases. Traditional agriculture often falls short due to limited arable land and water resources.
Vertical farming bridges this gap by utilizing vertical spaces, such as high-rise buildings and rooftops, for crop cultivation. This innovation plays a crucial role in enhancing food security by significantly increasing crop yield per square foot. Crops are grown in controlled environments, which means they are less susceptible to pests, diseases, and extreme weather conditions.
Furthermore, vertical farming facilities often integrate advanced technologies like hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. These systems minimize water usage, which is especially critical in water-scarce regions, by recycling and repurposing water efficiently. By reducing the need for pesticides and herbicides, vertical farming also promotes healthier, chemical-free produce that reaches the consumer faster and fresher than traditional farming methods.
This approach is not just beneficial for the environment; it’s transformative for urban communities. Vertical farms create local jobs and reduce transportation emissions associated with food logistics. As you see, vertical farming is not just a trend but a pivotal strategy towards achieving sustainable agriculture, meeting the demands of the future, and securing food for generations to come.
Quick Stats
- Urban vertical farms can reduce transportation emissions by up to 90% by growing food closer to consumers.
- Vertical farming can reduce land use by up to 99% compared to traditional farming.
- The global vertical farming market is projected to reach $12 billion by 2026.
- Vertical farming can produce yields up to 10 times higher per square foot compared to conventional agriculture.
- Vertical farms can reduce pesticide use by up to 100% as they often operate in controlled environments.
- Vertical farms can operate year-round, increasing productivity by up to 30%.
- The global vertical farming market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 24.6% from 2020 to 2027.
Maximizing Crop Yield With Vertical Farming
| Parameter | Traditional Farming | Vertical Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Land Use | Extensive | Minimal |
| Water Usage | High | 95% Less |
| Yield Increase | Baseline | Up to 200x |
| Pesticide Usage | Higher | Negligible |
| Climate Dependency | Dependent | Independent |
When comparing traditional and vertical farming, it’s clear that vertical farming presents a remarkable leap toward sustainable agriculture. Imagine producing significantly more food without the demands on vast land or excessive resources. Vertical farming provides a compelling vision for what the future of farming could look like—where innovation meets necessity.
Not only does vertical farming dramatically reduce the amount of water and land needed, but it also allows for consistent, year-round production regardless of external weather conditions. This is a true game-changer, especially in regions prone to harsh climates or where arable land is scarce.
The Science Behind Vertical Farming
When it comes to efficiency and resource management, vertical farming leverages cutting-edge technologies to create an optimal environment for crop production. A prominent feature is the use of hydroponics, a soil-free technique where plants grow in nutrient-rich water. This allows for precise control over diet and encourages faster growth cycles, significantly reducing land usage compared to traditional farming methods.
In tandem with hydroponics, aeroponics offers another soil-less solution where plant roots are consistently misted with nutrient solutions. This method enhances oxygen exposure, encouraging stronger and quicker plant development. Vertical farms frequently utilize a combination of both systems to cater to different crop needs.

Smart Technologies
To replicate natural sunlight, LED lighting is a game-changer. These energy-efficient lights are customizable to emit specific wavelengths conducive to photosynthesis. This targeted lighting promotes plant health and development while minimizing energy consumption. The adaptation of smart technologies ensures that these systems adjust based on plant requirements at different growth stages, optimizing resource usage.
Additionally, implementing advanced data analysis and monitoring systems assists in maintaining consistent environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels. These technological advancements help mitigate the risks associated with climate change by providing a consistently stable environment.
As urban populations grow, vertical farming not only prioritizes sustainability by reducing transportation emissions but also ensures food security through local production. Encouragingly, this method presents itself as a scalable model capable of reshaping the agricultural landscape and catering to future demands.
Harnessing Technology for Sustainable Farming
- LED Grow Lights: These lights mimic sunlight to facilitate plant growth, optimizing energy efficiency.
- Hydroponic Systems: This soil-less cultivation method conserves water while promoting healthier crop growth.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors and automation control systems monitor and regulate environmental conditions within vertical farms.
- Climate Control Technologies: Advanced HVAC systems manage temperature and humidity levels, ensuring optimal growing environments.
- Vertical Conveyor Systems: These systems maximize space efficiency, making it easier to transport and manage crops.