- This is the first in a series on this topic. Watch for our feature coverage of Yara Birkeland and Amazon Prime autonomous delivery and other features.
Autonomous Ships: The Quiet Revolution in Maritime Logistics
Autonomous ships represent a significant milestone in maritime logistics, promising safer and more efficient shipping solutions.

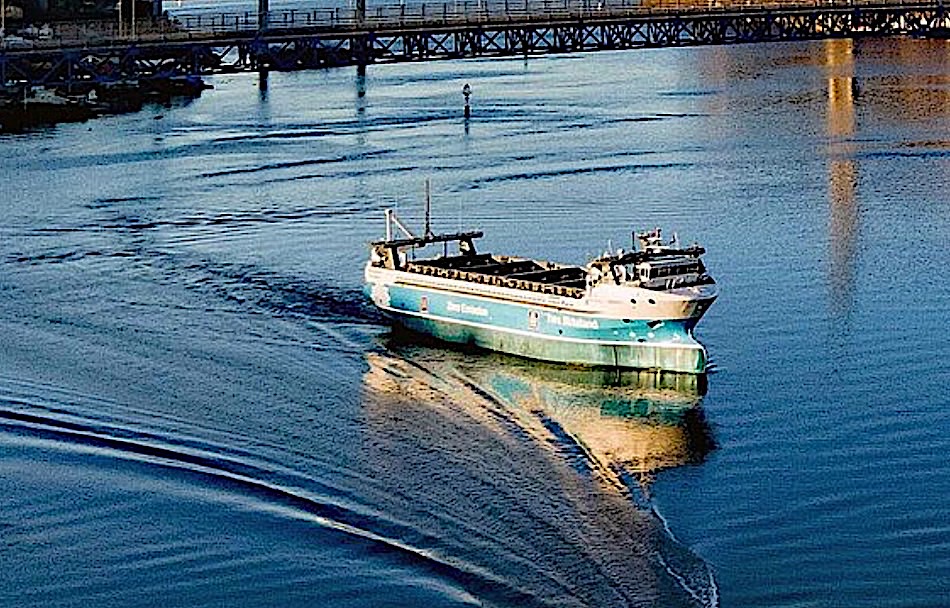
Case Study 1: Yara Birkeland
The Yara Birkeland, developed in Norway, is the world’s first fully electric, autonomous container ship. Powered by clean energy and advanced navigation systems, it aims to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and eliminate the need for crew onboard. This groundbreaking vessel is a testament to how autonomous technology can address sustainability challenges in shipping. (Source: Yara International)
Case Study 2: Rolls-Royce & Intel
Rolls-Royce, in collaboration with Intel, has created AI-powered unmanned vessels designed for safer, fuel-efficient maritime operations. These ships leverage cutting-edge AI to optimize routes, reduce operational costs, and minimize human error. (Source: Rolls-Royce)
Challenges
Despite their promise, autonomous ships face substantial challenges:
- Regulatory hurdles: International laws governing autonomous vessels remain underdeveloped.
- Cybersecurity risks: Unmanned ships are susceptible to hacking and data breaches, posing safety and operational risks.
Industrial & Warehouse Automation: Drones & Mobile Robots
The industrial sector is experiencing a revolution in automation through drones and mobile robots, enhancing efficiency in warehousing, logistics, and manufacturing.
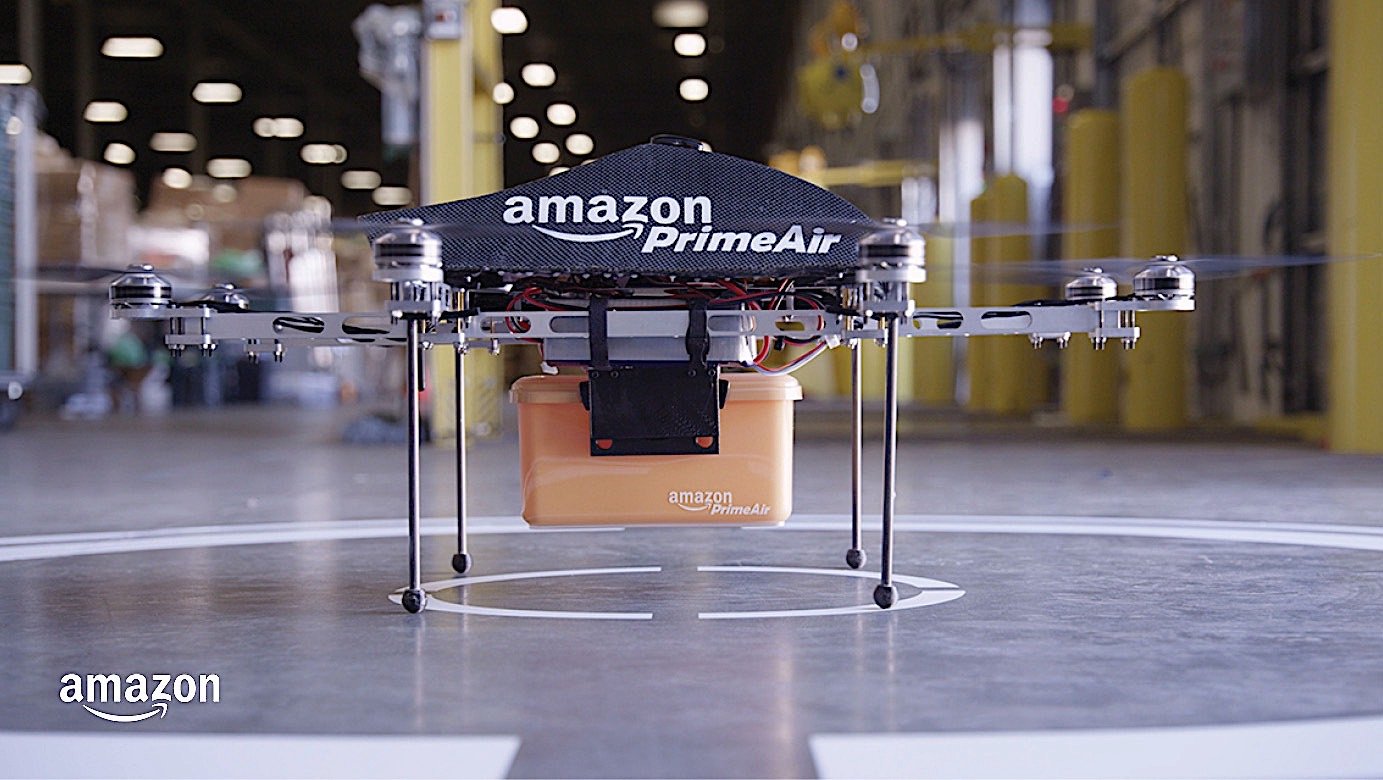

Case Study 1: Amazon Prime Air
Amazon’s Prime Air drones, approved for FAA trials, show the potential of autonomous systems in last-mile delivery. These drones navigate urban environments to deliver packages directly to customers’ doorsteps, reducing delivery times and operational costs. (Source: Amazon Newsroom)

Case Study 2: Boston Dynamics’ Stretch Robot
Boston Dynamics has introduced Stretch, a robot designed for warehouse logistics. Equipped with advanced sensors and AI capabilities, Stretch automates the process of loading and unloading, improving productivity and reducing human intervention. (Source: Boston Dynamics)
Trend: AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance
AI-powered systems in factories are now enabling predictive maintenance, wherein data collected from machinery is analyzed to forecast potential failures. This trend reduces downtime and optimizes production lines, further demonstrating the power of autonomous technology.
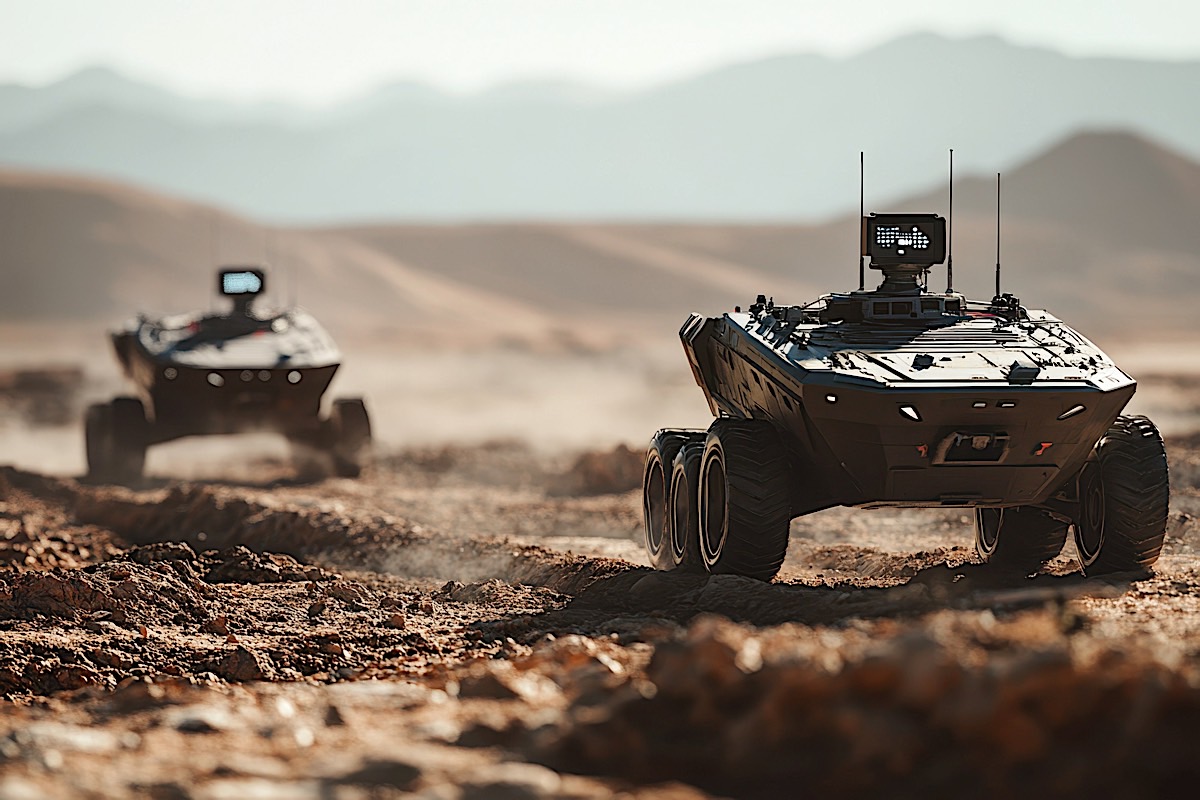

Military & Defense: The AI Battlefield
Autonomy has emerged as a critical force in military and defense strategies, with AI-driven systems transforming the operational landscape.
Case Study 1: US Navy’s Sea Hunter
The Sea Hunter, an autonomous submarine-tracking warship developed by DARPA, represents a new era of unmanned naval defense. Capable of operating independently for extended periods, it enhances the U.S. Navy’s surveillance capabilities while reducing risks to personnel. (Source: DARPA Program)
Case Study 2: Turkish-Made Kargu-2 Drones
Turkey’s Kargu-2 drones, equipped with AI-powered loitering munitions, have been deployed in various conflicts. These drones autonomously identify and engage targets, showcasing how AI is revolutionizing modern warfare. (Source: UN Report)

The Future: Where Are We Heading?
The trajectory of autonomous systems suggests profound changes across industries. Some predictions include:
- Fully autonomous ports: By 2030, ports like Singapore’s Tuas Port are expected to operate entirely autonomously.
- Swarm drone technology: Swarm drones may revolutionize disaster response and agriculture, coordinating en masse for efficient results.
Key Hurdles
However, certain obstacles remain:
- Public Trust: Ensuring safety and reliability of autonomous technologies is crucial for widespread acceptance.
- Legal Frameworks: Current laws governing these systems need modernization to address ethical and operational concerns.
- AI Reliability: Improving AI’s decision-making capabilities is essential to avoid errors and unintended consequences.
Question for Readers
Which industry do you believe will be most transformed by autonomy next? Share your thoughts and join the conversation on these groundbreaking innovations!
Sources & Citations
- Yara Birkeland – Yara International Press Kit
- Rolls-Royce Autonomous Ships – Rolls-Royce News
- Amazon Prime Air Drones – Amazon Newsroom
- Boston Dynamics Stretch Robot – Boston Dynamics
- US Navy’s Sea Hunter – DARPA Program
- Kargu-2 Drones in Conflict – UN Report on Libya