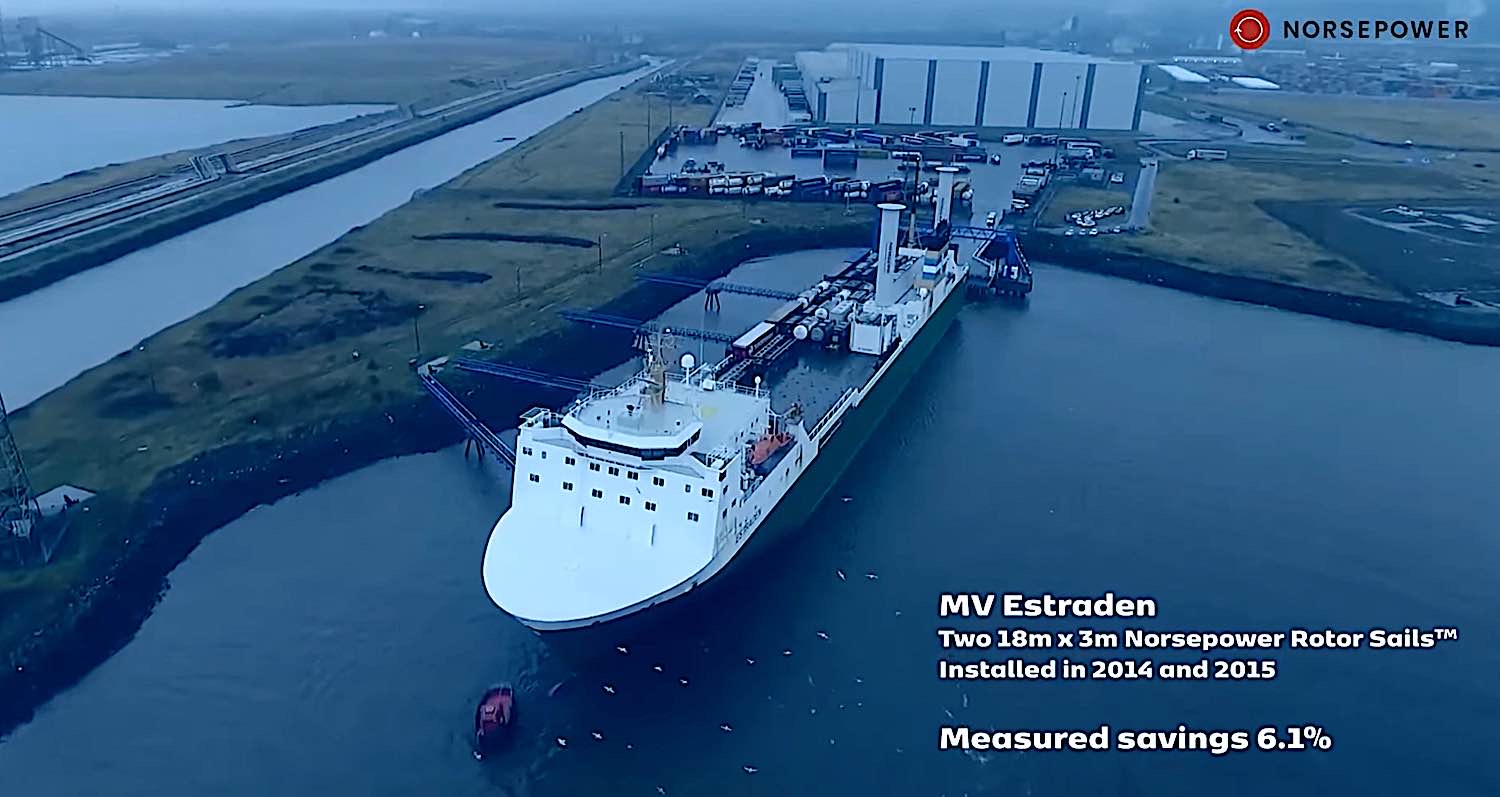
Visualize the future of sail in shipping: a vast expanse of the ocean, dotted with a new generation of sleek, streamlined vessels, their sails spinning in the wind. These sails are no ordinary sails billowing in the breeze; they are advanced rotor sails, an ingenious blend of old and new, allowing the shipping industry to harness wind power in an innovative leap towards sustainable transportation.
This isn’t just “a visualization.” More than 100 ships already exploit this breakthrough engineered design, aand it is predicted that the ongoiing connversion and retrofitting of existing ships will saave $200 billion in fuel costs by 2050.

Quick Facts on Future Wind-Power for Shipping
- Modern wind-powered ships use technologies such as Flettner rotors, wing sails, and kite sails.
- Wind-powered shipping is not a new concept; it was the primary means of maritime transport until the 19th century.
- Flettner rotors are tall, spinning cylinders that use the Magnus effect to generate a force perpendicular to the wind direction.
- Wind-powered shipping reduces reliance on fossil fuels, contributing to lower carbon emissions.
- According to the International Maritime Organization, shipping contributes to about 2.5% of the world’s total greenhouse gas emissions.
- Wind-powered shipping can reduce a vessel’s fuel consumption by 10-30%, and up to 50% under optimal conditions.
- Wind propulsion technologies can be retrofitted onto existing ships or incorporated into new ship designs.
- Wind-powered ships are quieter and cause less disturbance to marine life compared to conventional ships.
- Challenges to wind-powered shipping include variable wind conditions, increased ship handling complexity, and initial investment costs.
Innovative Engineering: Auxiliary Wind Propulsion
From an engineering perspective, these are not the archaic wooden ships of old, but high-tech vessels engineered with cutting-edge technology. According to Norsepower, a leading provider of low-maintenance, software-operated, and data-verified auxiliary wind propulsion systems, the mechanism is based on the Flettner rotor—a spinning cylinder that uses the Magnus effect to capture wind power and propel the ship. This rotor sail technology presents a tested, verified, and economical way of reducing the carbon footprint of commercial shipping.
“This is not just a step, but a leap towards sustainable shipping. By harnessing wind power, we can significantly reduce CO2 emissions and the reliance on fossil fuel.”
– Tuomas Riski, CEO of Norsepower
- Utilizing the Magnus effect: The spinning cylinders atop the ship’s deck leverage this aerodynamic phenomenon to create a pressure differential—the key to propulsion.
- Minimalistic design: The unobtrusive design of modern rotor sails allows them to be retrofitted onto existing vessels, or integrated into designs of new ships.
- Automation: The latest systems operate autonomously, analyzing weather data in real time to optimize sail position for maximum efficiency.
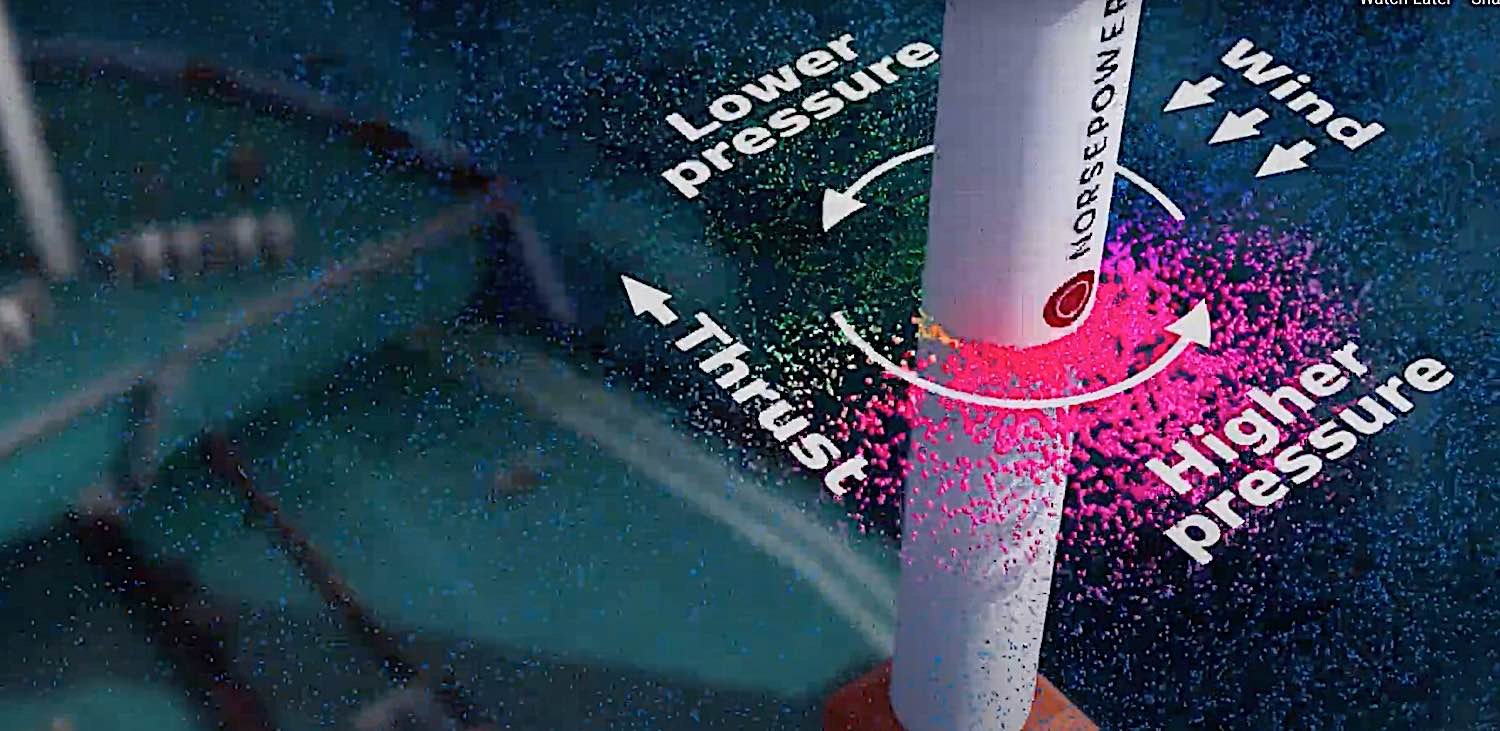

This revival of wind power in shipping, from an engineering and innovative standpoint, marks a return to traditional wisdom married with cutting-edge technology. It’s evidence that, in the world of sustainable transportation, sometimes we need to look backwards to propel ourselves forward.

The Green Statistics
Here are some hard facts that support the return to a form of wind propulsion at sea:
- Wind propulsion systems can reduce fuel consumption and CO2 emissions by 10-30%
- In 2018, the International Maritime Organization (IMO) set a target to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from shipping by at least 50% by 2050
- Wind-powered shipping could save approximately $200 billion in fuel costs by 2050
- Modern wind-powered ships can reach speeds of up to 16 knots
- The global wind propulsion systems market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.2% from 2021 to 2026
- There are currently over 100 wind-assisted ships in operation worldwide

How Wind-Powered Shipping Reduces Carbon Emissions
Imagine if we could commandeer the forces of nature, to harness the wind that fills the sails, and use that same power to propel massive, industrial-grade ships across the oceans. Well, you don’t have to imagine it any longer, as wind-assisted propulsion technology is showing us that it’s possible.
Engineering-wise, this is made possible by using either wind capture devices or specially designed sails to optimize wind energy. In flicking the switch towards wind-assisted propulsion, the maritime industry has been able to leverage an age-old method packed with modern technological advancements while contributing to environmental stability.
Let’s delve a bit deeper. Each ship equipped with wind-assisted technology contains either a fixed or rotatable wing sail or kite sail. When wind hits these sails, it generates a forward thrust, aiding the main engine in propelling the ship. This combo of sails and engine results in decreased fuel consumption; this is important because lesser fuel consumed means lower carbon emissions.
Take, for instance, the ‘Oceanbird’ concept, where the ship is powered by towering wing sails reaching skywards. These sails are interwoven with sensors, computers, and hydraulic systems that let them be angled optimally in real-time, maximizing the use of wind and minimizing emissions by a staggering 90%[Source].
But, there’s more than just decreasing fuel consumption. Wind-assisted propulsion systems also lend a hand in attenuating greenhouse gas emissions and carbon taxes. Increased use of wind power not only significantly lowers the emission of carbon dioxide but also the release of harmful sulfur and nitrogen oxides into the environment[Source Science Direct].
While commitment from cargo owners is essential to ensure the successful adoption of wind-assisted propulsion, it’s nonetheless clear that these new-generation technologies are taking giant strides toward a greener and more sustainable future of shipping.

Wind vs Fuel: A Comparative Analysis
With increases in technology, we now look to the wind – a source of greener and more sustainable power – and compare it with the conventional fuel used in the shipping industry. Let’s explore the differences between these two power sources in terms of efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and ecological impact.
| Wind-Assisted Propulsion | Traditional Fuel Propulsion | |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | Wind contributes significantly to total propulsion, reducing fuel consumption. Wind systems can offer fuel savings from 8% to 30% on global shipping routes. | Dependent on fossil fuels, which are finite resources. Operational efficiency can be subject to fluctuating fuel prices and availability. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Potential cost savings from reduced fuel consumption. However, initial setup costs can be substantial. Over time, operational costs may decrease due to lower fuel dependency. | Fuel costs are constantly rising, and these comprise a significant portion of operational costs. Additionally, regulatory fines for emissions can also add to overall expenses. |
| Ecological Impact | Drastically reduces carbon emissions and shrinks the carbon footprint of the maritime industry. Notably, it also mitigates the cost of carbon taxes. | Fossil fuel use releases significant greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change. Stricter emission standards impose extra costs for carbon-based fuels and related technologies. |
Although the transition will require initial investment and time, the benefits of wind-assisted propulsion ultimately tip the scales in its favor when considering a sustainable and efficient shipping future.