Engineering wearable technology for a safer and more efficient workforce
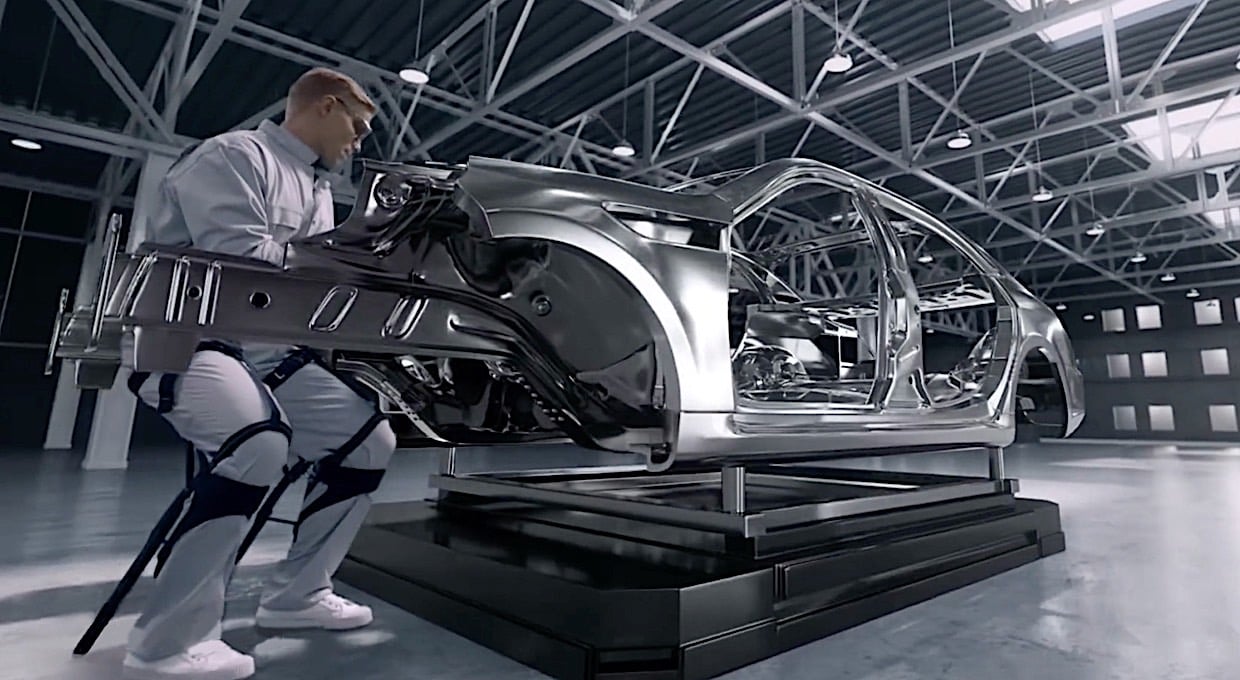
Exoskeleton technology has emerged as a transformative solution for labor-intensive industries, offering new opportunities for engineers to innovate. Wearable robotic exoskeletons, designed to enhance human strength and endurance, are redefining physically demanding tasks in sectors like manufacturing, construction, and logistics.
Hyundai Motor Group and Sarcos Robotics are at the forefront of developing these advanced systems, combining engineering ingenuity with practical applications to improve workplace safety and efficiency.
Quick Facts
- Hyundai Motor Group collaborates with Sarcos Robotics to pioneer wearable exoskeleton technology.
- Wearable robotic exoskeletons are designed to enhance strength, endurance, and workplace safety.
- The Hyundai Vest Exoskeleton (H-VEX) offers support for overhead tasks like welding and assembly.
- The Hyundai Chairless Exoskeleton (H-CEX) provides ergonomic solutions for static postures and lower-body strain.
- Musculoskeletal disorders account for 38% of global work-related health issues, according to the ILO.
- Advanced robotics and sensor integration allow exoskeletons to adapt intelligently to user movements.
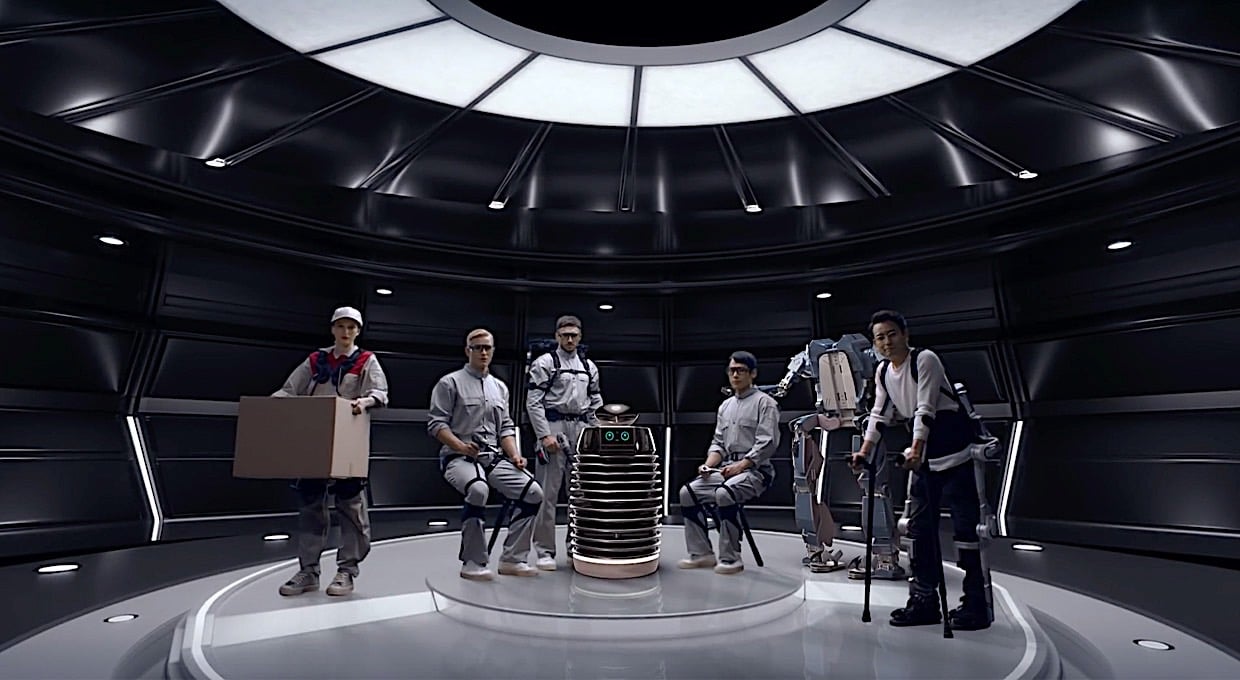

The Promise of Wearable Exoskeletons
Exoskeletons represent a breakthrough in assistive technology, merging mechanical engineering with human ergonomics. These wearable devices act as robotic frameworks that augment a worker’s physical capabilities, enabling them to perform repetitive movements, heavy lifting, or prolonged postures with reduced strain and decreased risk of injury. For engineers, these innovations showcase the possibilities of robotics and sensor integration, while educators can use them as case studies to engage students in mechanical design and human factors engineering.
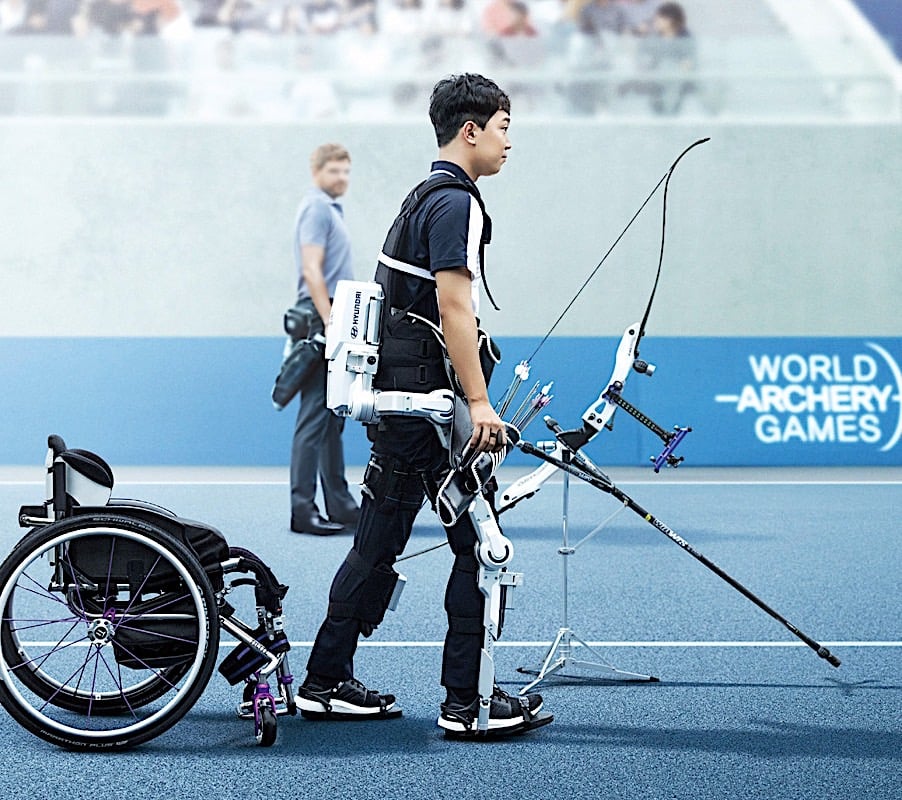

Addressing Workplace Injuries
Work-related injuries, particularly musculoskeletal disorders, remain a significant challenge in labor-intensive roles. According to the International Labor Organization (ILO), musculoskeletal disorders account for nearly 38% of global work-related health issues. Exoskeletons provide a scientifically validated solution to mitigate these risks, reducing physical stress on the body through intelligent systems that adapt to user movements. Hyundai and Sarcos Robotics have integrated advanced engineering principles into their designs to ensure these devices align with ergonomic best practices.

Hyundai Motor Group’s Exoskeleton Innovations
Hyundai Motor Group’s commitment to wearable robotics reflects their focus on innovating practical solutions for industrial applications. Their exoskeleton designs, such as the Hyundai Vest Exoskeleton (H-VEX) and Hyundai Chairless Exoskeleton (H-CEX), demonstrate how mechanical systems can be tailored to solve specific workplace challenges while meeting rigorous engineering standards.
Hyundai Vest Exoskeleton (H-VEX)
The H-VEX is optimized for overhead tasks, such as welding or component installation. Its lightweight design incorporates mechanical supports for arms and shoulders, alleviating strain during repetitive movements. Engineers can appreciate its precision in load redistribution and posture stabilization, while educators may highlight its potential to demonstrate applied robotics and biomechanics.
Hyundai Chairless Exoskeleton (H-CEX)
The H-CEX addresses challenges faced in static postures, such as squatting or prolonged standing, by providing ergonomic support to the knees and lower back. Adjustable leg supports and customizable fittings ensure optimal comfort and effectiveness. This device exemplifies how engineering can resolve chronic pain issues while offering a practical teaching tool for ergonomic design principles.
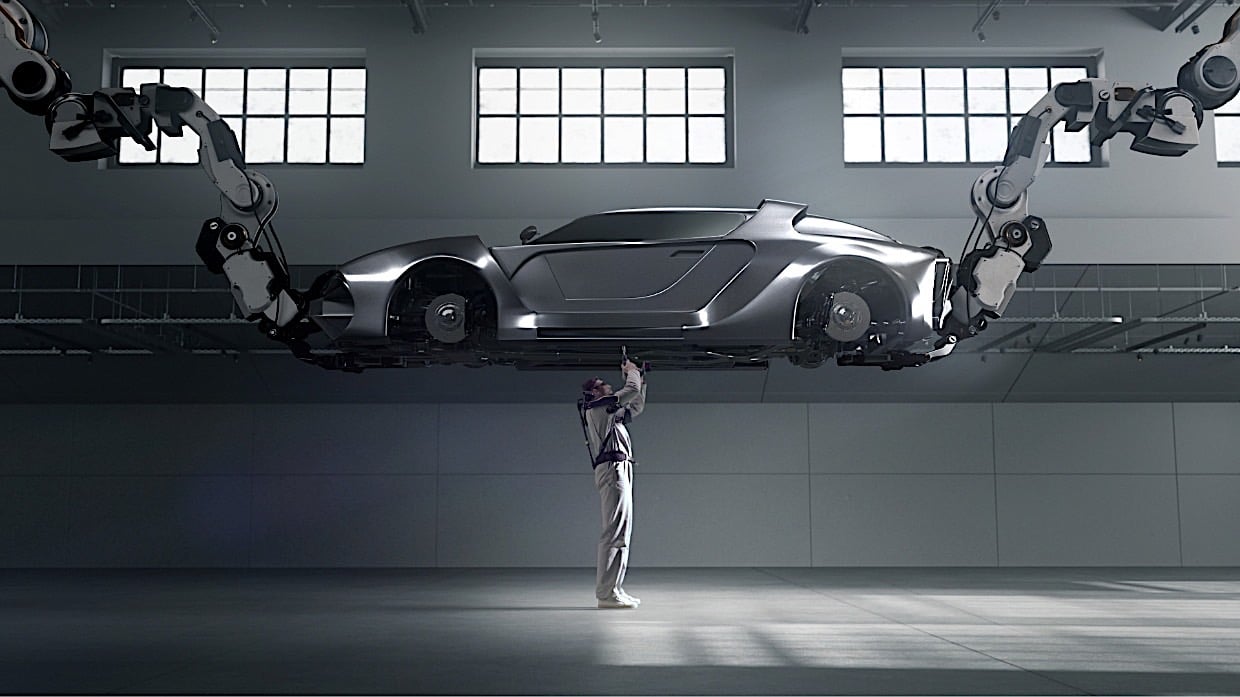
Sarcos Robotics and the Future of Wearable Tech
Sarcos Robotics stands as a leader in industrial wearable technology, with its Guardian XO and Guardian XT systems setting benchmarks for strength and adaptability. These innovations showcase the interplay between mechanical precision and human intelligence, offering versatile applications for engineers and educators alike.
Guardian XO
Designed for heavy-duty industries, the Guardian XO is a full-body powered exoskeleton capable of lifting up to 200 pounds. Its adaptive mechanisms and intuitive controls illustrate the art of engineering user-friendly robotics, making it a prime example for educators to discuss usability and design optimization. Its applications in construction and logistics highlight its real-world relevance.
Guardian XT
The Guardian XT focuses on tasks requiring precision and reach, such as electrical wiring, assembly, and inspection. Its robotic arms mimic user motions with exceptional accuracy, showcasing engineering ingenuity in kinematics. For educators, the XT serves as a demonstration of how advanced robotics can address industrial challenges while maintaining durability and flexibility.
Collaboration for a Safer Workforce
Hyundai and Sarcos Robotics emphasize the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration in the development of exoskeletons. By merging robotics expertise with ergonomic considerations, they aim to create devices that are user-friendly, effective, and adaptable across various industries. Educators can leverage this collaborative approach as an example to inspire cross-disciplinary learning among students.
Integration with Artificial Intelligence
The integration of AI into exoskeleton technology represents the next frontier in wearable robotics. Hyundai and Sarcos are pioneering intelligent systems that predict user fatigue, optimize movements, and perform predictive maintenance on devices. These advancements hold immense potential for engineers seeking innovation in automation and educators teaching the future of smart systems.
Challenges and Opportunities
Despite their potential, widespread adoption of exoskeletons faces challenges such as cost and required training. Engineers must focus on cost-efficient designs, while educators can explore ways to simplify device operation through training modules. Overcoming these barriers will unlock immense opportunities, paving the way for applications in healthcare, defense, and rehabilitation.
Final Thoughts
Wearable exoskeleton technology, driven by Hyundai Motor Group and Sarcos Robotics, is revolutionizing labor-intensive industries. For engineers, these systems exemplify the intersection of mechanics, robotics, and human-centered design. For educators, they offer rich potential to inspire the next generation of innovators. As the field of engineering design continues to evolve, exoskeletons stand as a testament to the power of collaboration and the limitless possibilities of technological advancement.
Citations
– International Labor Organization. “Work-related Musculoskeletal Disorders: Prevention and Control.”
– Hyundai Motor Group. “H-VEX and H-CEX: Transforming Manufacturing with Wearable Robotics.”
– Sarcos Robotics. “Guardian XO and Guardian XT: Revolutionizing Heavy Industry.”
Pursuant to the Creative Commons License (CCL) 2.0, all users can copy, distribute, and transmit Information available on the Hyundai Motor Group Newsroom, or use it for exhibitions and performances.