Robotics in modern manufacturing is not just a trend; together with AI, it is world-changing. According to the ROBO Global Report, the industrial automation market is projected to grow from $16.9 billion in 2020 to $25.18 billion by 2028. In the last decade, robots in manufacturing increased by 85 percent These data points emphasize how robotics is driving unprecedented change in the manufacturing landscape.
“The convergence of AI, robotics, and traditional manufacturing is creating a new era of automated processes, reducing human error and increasing overall efficiency.” – ROBO Global.

The story of Robotics by the Numbers
From collaborative robots (cobots) to full automation, the use of robotics in manufacturing is supported by the numbers:
Robots in manufacturing have increased by 85% in the past decade.
Robots can increase productivity by up to 30% in manufacturing processes.
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) can reduce material handling costs by 25%.
Robots can reduce defects in manufacturing by up to 80%.
Ten Innovative Applications of Robotics: From 3D Printing to Material Handling
Robotics advancements in manufacturing are paving the way for various innovative applications. Here are ten compelling examples redefining efficiency and productivity:
1. 3D Printing – Autodesk’s robotic arm Dreamcatcher is overhauling the 3D printing process by providing precise control of multi-axis printing, fostering intricate designs.
2. Material Handling: Flexion’s N-Series collaborative robots (cobots) have high payload capacities, improving safety and efficiency in material handling operations.
3. Painting – ABB’s RobotStudio is transforming painting processes by providing reliable precision and eliminating the risks of exposure to toxins for human employees.
4. Welding – Robotic welding systems are boosting productivity by taking over tedious tasks while offering improved stability and quality in welding.
5. Product Inspection – Cognex’s Machine Vision robots efficiently inspect products with increased accuracy for defects, maintaining high-quality standards.
6. Pharmacy Automation – ARxIUM’s RIVA system uses robotics in preparing and dispensing medications, reducing human error and increasing efficiency in pharmacies.
7. Electronics Assembly – Universal Robots’ UR3 robotic arm performs sensitive electronics assembly tasks with high precision, improving product quality and production speed.
8. Packaging – Adept Technology’s Quattro s650H robots are redefining packaging processes with speed and flexibility, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput.
9. Precision machining – KUKA’s KR QUANTEC robots are optimizing CNC machining by providing flawless precision.
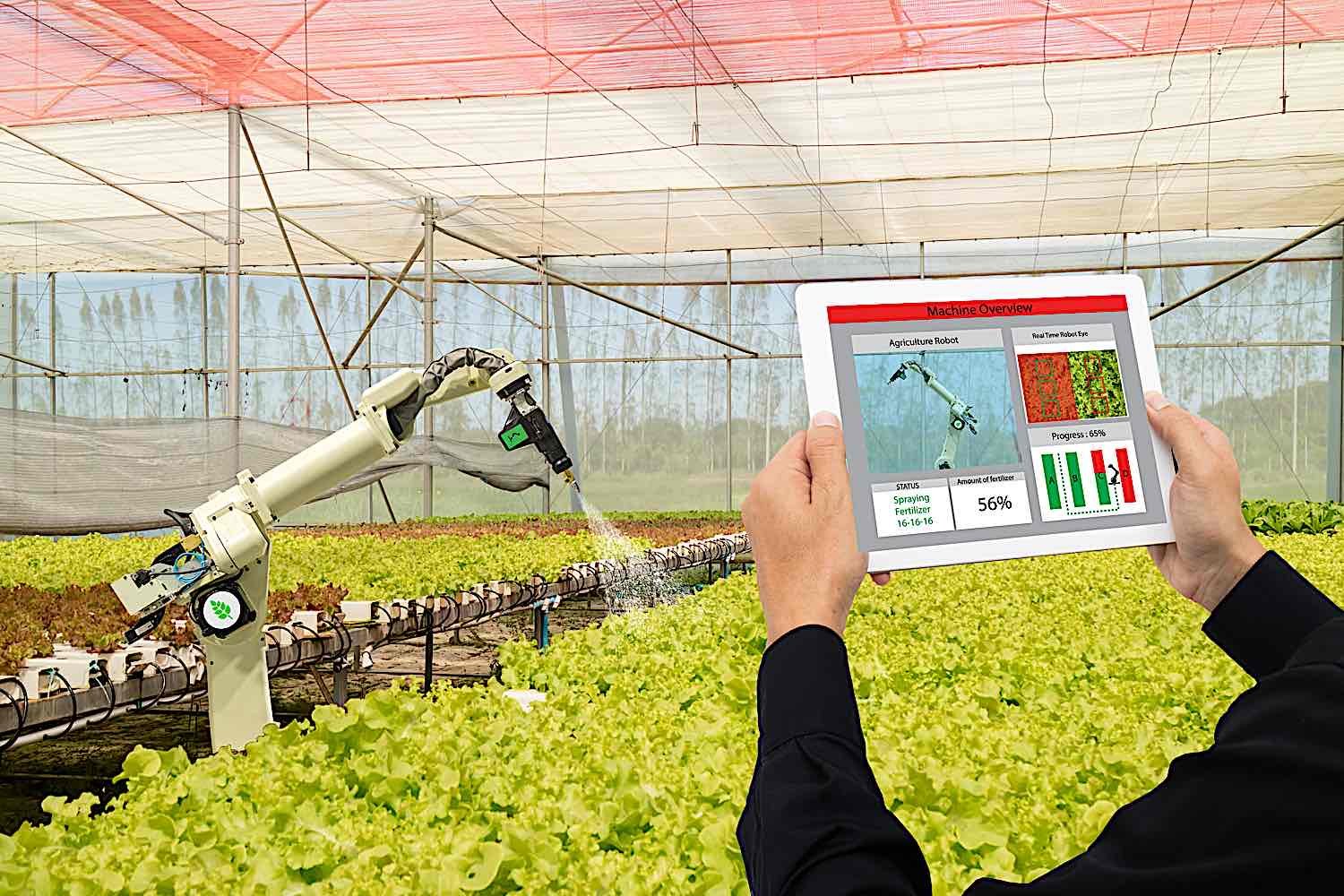
10. Agriculture – Harvest CROO’s autonomous robots are revolutionizing the agricultural industry with automated strawberry harvesting, demonstrating an expansion of robotics beyond the traditional manufacturing setting.
These examples illustrate the vast potential of robotics, providing a remarkable boost to manufacturing productivity and efficiency. As technology continues to develop, it is exciting to see what other innovative applications will emerge in the robotics space.
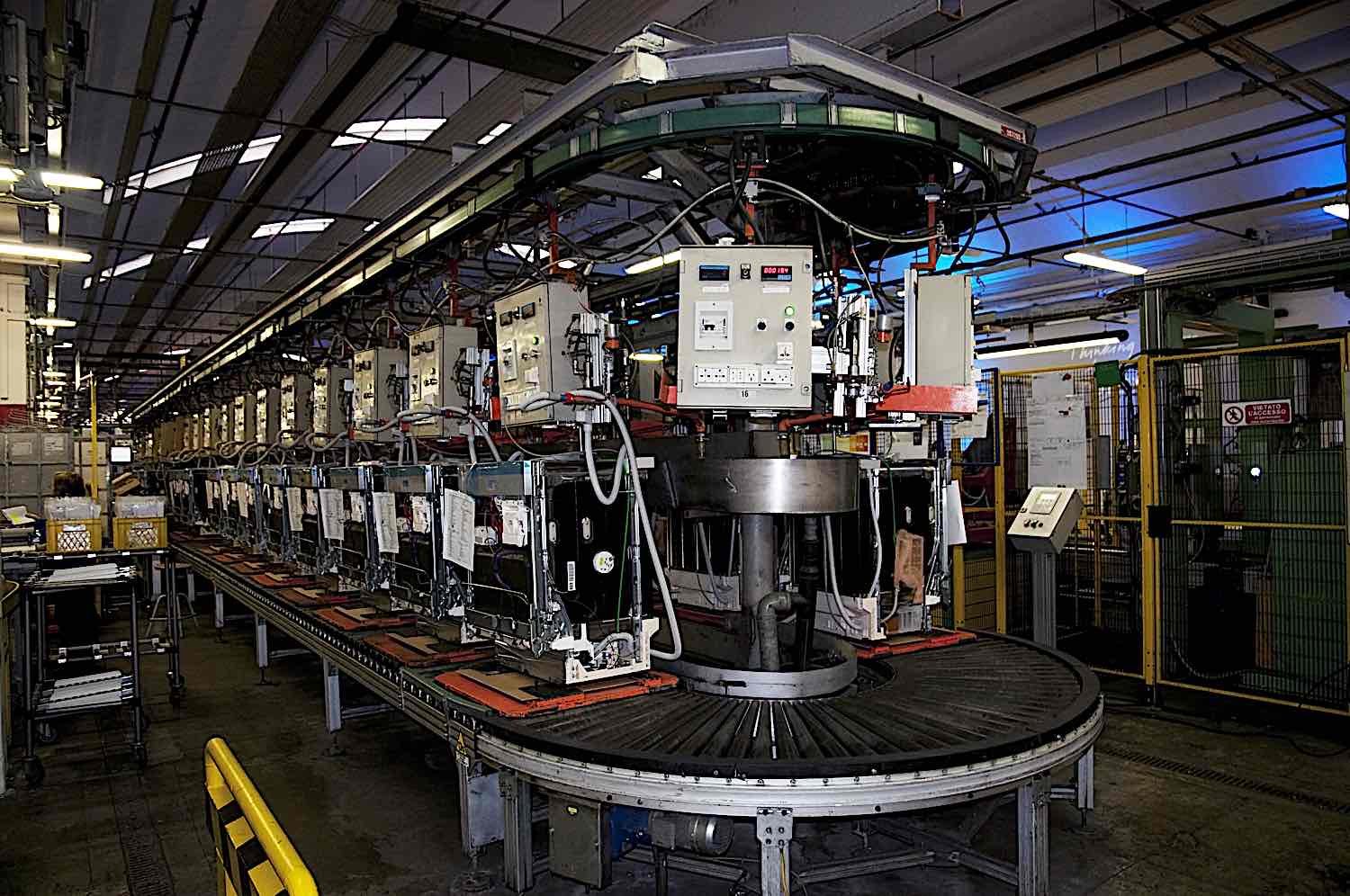

The Impact of Robotics on Efficiency and Productivity in Manufacturing
We can’t talk about robotics and manufacturing without considering the remarkable improvements in efficiency and productivity that these technologies have brought along. Simply put, robots ensure jobs get done faster and more precise than ever before. But how exactly do they achieve this?
The introduction of robotics has revolutionized modern manufacturing by enabling faster production cycles, reducing errors, and improving overall efficiency.
– Cynthia Breazeal
Robots allocate human resources more efficiently. They perform repetitive and mundane tasks, leaving humans free to focus on tasks that require critical thinking and creativity. This way, robots increase the overall productivity by reducing the likelihood of human errors while at the same time speeding up the production process. According to a study by McKinsey, automation can increase productivity growth by 0.8 to 1.4 percent annually.
Secondly, robotics streamline and automate processes, eliminating unnecessary steps and therefore improving assembly line efficiency. Robots utilize a combination of sensors and software to accomplish precise movements and actions, reducing the time it takes to perform a task. This precision also increases the quality of the end product. In the aerospace industry, robots are used for tasks that require high precision such as drilling and riveting (See this article. )
No breaks for robots
Robots are also designed to work 24/7 without any breaks, increasing production capabilities. They can be programmed to work round the clock, which humans, even under the best conditions, cannot match.
Finally, robots achieve a higher level of safety in manufacturing environments by taking over hazardous tasks. By taking over potentially dangerous tasks, such as handling of chemicals or heavy machinery, they reduce the risk of work-related injuries, thereby elevating efficiency and productivity.

Enhancing Workplace Safety through Robotics in Manufacturing
To say that robotics enhance safety in the manufacturing workplace may be an understatement. The integration of robotics in manufacturing processes has led to a radical improvement in safety conditions for human operators. By taking on tasks that are often classified as “3D” – Dull, Dirty, or Dangerous – robots significantly reduce the risk of injuries and accidents in the workplace. But how exactly do they do this? Let’s dive into the details.
Dull Tasks
Robots are perfect for tasks which require repetitive motion – they don’t get bored or tired. Such tasks, including assembly line duties or quality checks, often lead to physical and mental fatigue in humans, increasing the risk of attention lapses and mistakes.
According to a study by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), ergonomic injuries due to repetitive motion, including musculoskeletal disorders, account for approximately one-third of the total occupational illnesses and injuries. By delegating these monotonous tasks to robots, we can reduce the occurrences of these injuries, leading to a safer and more efficient workplace.
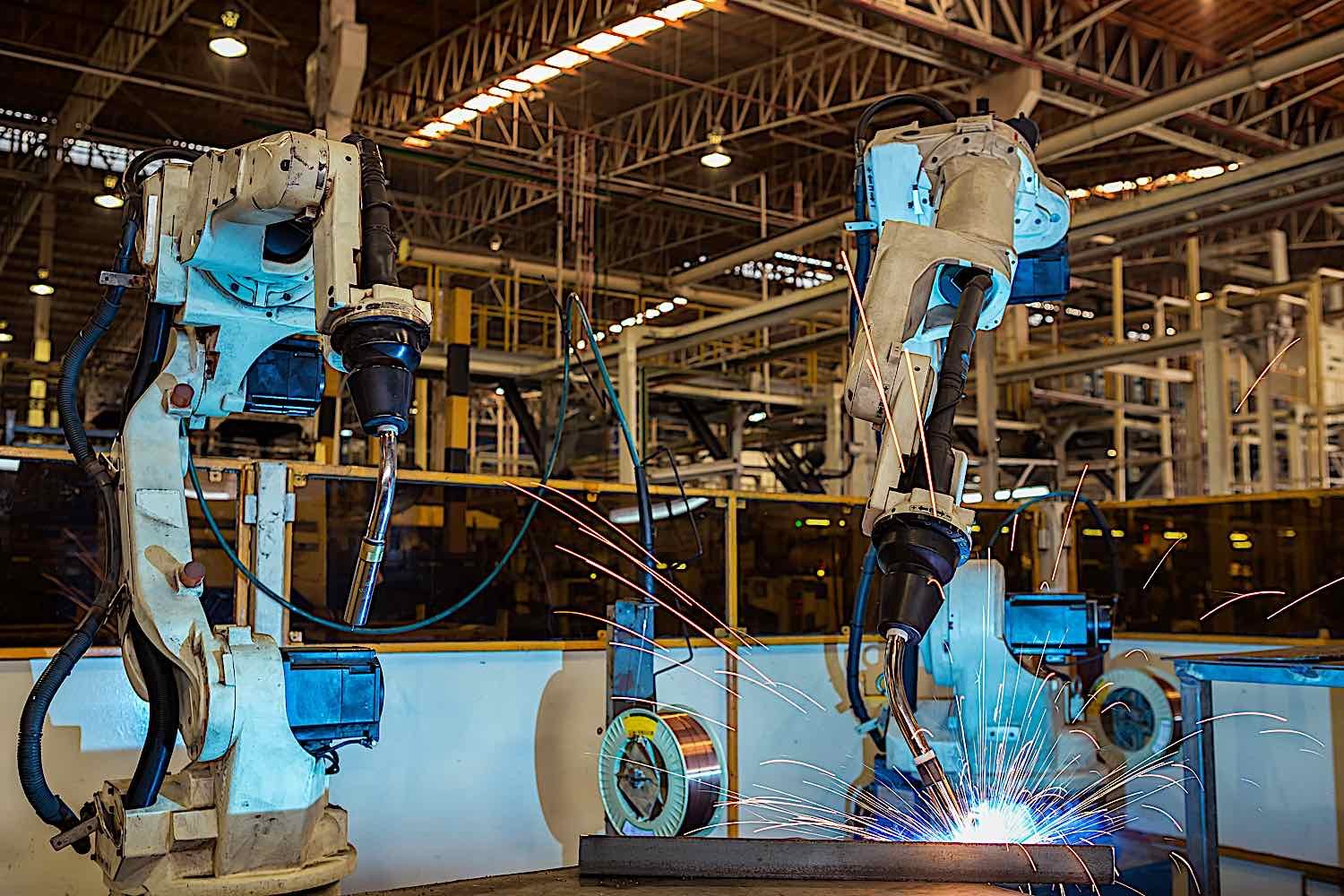

Dirty Tasks
Robots are also being deployed in environments that are hazardous to human health. Whether due to chemical hazards, extreme temperatures, or excessive noise, robots are immune to these threats, making them the perfect solution for jobs that involve working under such harmful conditions.
An example of this is the robots at Ultratech Cement, one of the largest cement manufacturers in India, who perform dangerous tasks such as refractory lining in cement kilns under extreme heat conditions, reducing the risk of heatstroke or burns which were previously faced by human workers.
Dangerous Tasks
Tasks that involve a high risk of severe injuries or fatalities have also been increasingly taken over by robots. Robots are now being used to perform tasks such as heavy lifting, working at heights, or handling hazardous materials, thereby greatly minimizing the risk of severe injuries and fatalities.
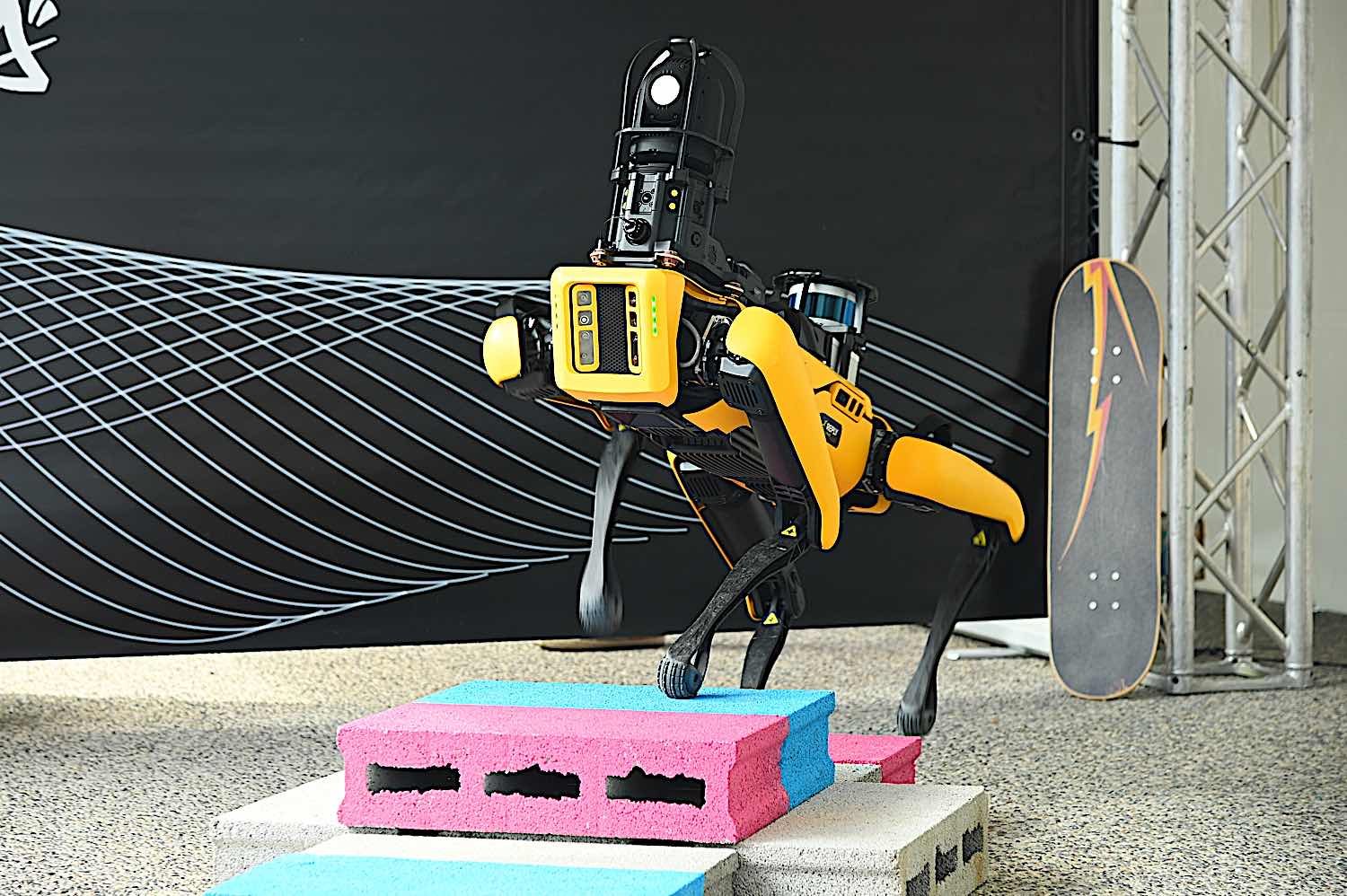

Spot from Boston Dynamics
Boston Dynamics’ robot ‘Spot’ which is used for inspecting dangerous, inaccessible, or hazardous areas in manufacturing environments. This use of robotics provides an increase in efficiency and safety simultaneously. Rather than an individual potentially risking injury, a ruggedized and versatile robot such as ‘Spot’ can enter these areas, perform detailed inspections, and relay the information back to handlers in a safe location. The Boston Dynamics website provides more extensive information about Spot’s capabilities in various industrial settings.
Flexibility and Customisation of Robotic Solutions
Robots in manufacturing are not one-size-fits-all solutions. Instead, they typically offer a degree of customisation that allows for adaptation to specific tasks or environments. For example, FANUC offers a wide range of collaborative robots – or cobots, designed to work side-by-side with human operators in manufacturing. Different models, arm lengths, and payload capacities can be selected based on the requirements of the tasks they are expected to perform.
Automation is not about replacing humans, it is about amplifying their capabilities and allowing them to focus on higher value tasks.
– Satya Nadella
Robotics and Quality Control
Another area where robotics are transforming manufacturing is in quality control. Traditionally, this process was largely manual and labor-intensive. But with advancements in robotics and machine vision systems, robots can now perform these tasks with greater precision and consistency. For example, the Cognex machine vision system is designed to provide fast and accurate inspections, even in challenging manufacturing conditions. This ultimately leads to higher quality products and increased efficiency.
The Role of Robotics in Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
When it comes to sustainable manufacturing, robotics offers immense potential, significantly reducing waste, optimizing resource use, and minimizing environmental impact. Particularly in areas such as precision manufacturing and smart waste management, the role of robotics is growing increasingly key to realizing these goals.
Within precision manufacturing, robots are known for their high level of accuracy and consistency. Such precise operation leads to substantial reductions in material waste. For instance, Swedish-Swiss multinational corporation ABB is renowned for its industrial robotics solutions which enable precision manufacturing.

Robots in smart waste management
Robots are employed in smart waste management in the manufacturing sector. Companies are deploying robotic systems for sorting recyclable materials and managing waste more efficiently. An example is AMP Robotics, a company that produces AI and robotics systems for the recycling industry. Their robotic systems can identify and sort various recyclable materials, which not only increases recycling rates but also minimizes landfills, thus promoting sustainability.
Robots can work in conditions that are hazardous for human workers, further cementing their role in advancing sustainable practices. Robotics technologies can replace humans in such tasks, as demonstrated by Boston Dynamics with their Spot robot—a quadruped robot able to navigate rugged terrains and operate in dangerous environments. This demonstrates how robotics can deliver operational efficiencies while protecting the health and safety of human workers.
The integration of robotics into manufacturing processes provides a pathway toward more sustainable industrial practices. From precise cutting and waste reduction to smart waste management and safe operation in hazardous conditions, robotics are playing a key role in advancing sustainability in manufacturing.
History: How Robotics Transformed Automotive Assembly Lines
In the realm of manufacturing, the automotive industry stands out as a pioneer in embracing automation. The assembly lines of auto-manufacturers have drastically evolved with the adaption of robotics. Arguably, no other industry has been as transformed by robotics as the auto-manufacturing sector, with automakers such as Ford, Toyota, and Volkswagen leading the charge. [source]
Starting as early as the 1960s, automobile manufacturers started toying with the idea of integrating computers and robots into their assembly lines. The outcome was remarkable. One shining example is Ford’s automated assembly line. Ford teamed up with KUKA, one of the leaders in industrial robotics, to automate most of their assembly operations – including welding, painting, and other repetitive, mundane tasks. The implementation of robotics has improved Ford’s production efficiency by reducing assembly line errors and decreasing production time. [source]
German automaker Volkswagen took the application of robotics in assembly lines to a different level. They introduced a human-robot collaboration program termed ‘collaborative robots’ (CoBots) on their assembly lines. These specially designed robots can work alongside their human co-workers, performing repetitive tasks while humans concentrate on complex ones. This combination of human intelligence and robotic precision significantly minimised errors and increased production rates. [source]
Toyota, a name synonymous with quality and innovation in the auto industry, is revolutionizing manufacturing with its Toyota Production System (TPS). In the heart of TPS is the concept of ‘kaizen’ or continuous improvement, where they continually refine and re-engineer their manufacturing processes, including the application of robotics. Toyota uses robotics not only for assembly tasks but also for inspecting and ensuring quality in every stage of the manufacturing process. [source]