With the world still deep in the grips of an energy crisis and ever-growing environmental concerns, the need for sustainable and renewable energy sources has become more urgent than ever.
Every country is looking for ways to reduce its dependence on fossil fuels and investing heavily in research for new alternative renewable energy sources.
We have many to choose from — each with its own issues, including the economics of production. [See the section “What alternative energy sources do we have today? below for a recap — see our extensive Green Energy section at EDI>>]
Spine-like Waveline Magnet generators may change that — with a low-cost production profile indicated, easy to maintain, and able to endure the worst ocean weather. It is a form of “wave energy” but with an exciting new promise — cost-effectiveness.
Video demonstrating the Sea Wave Energy Limited Waveline magnet concept:
The manufacturer claims:
“The Waveline Magnet’s has an inherently low cost of manufacture due to the low mass of materials used, such as plastics and reinforced plastics. SWEL’s technology uses materials and components that can be found and supplied without the need for new specialised production lines or a huge new infrastructure to accommodate it. This keeps the cost of production very low and due to its modular lightweight design the cost of deployment and retrieval are also drastically reduced.”
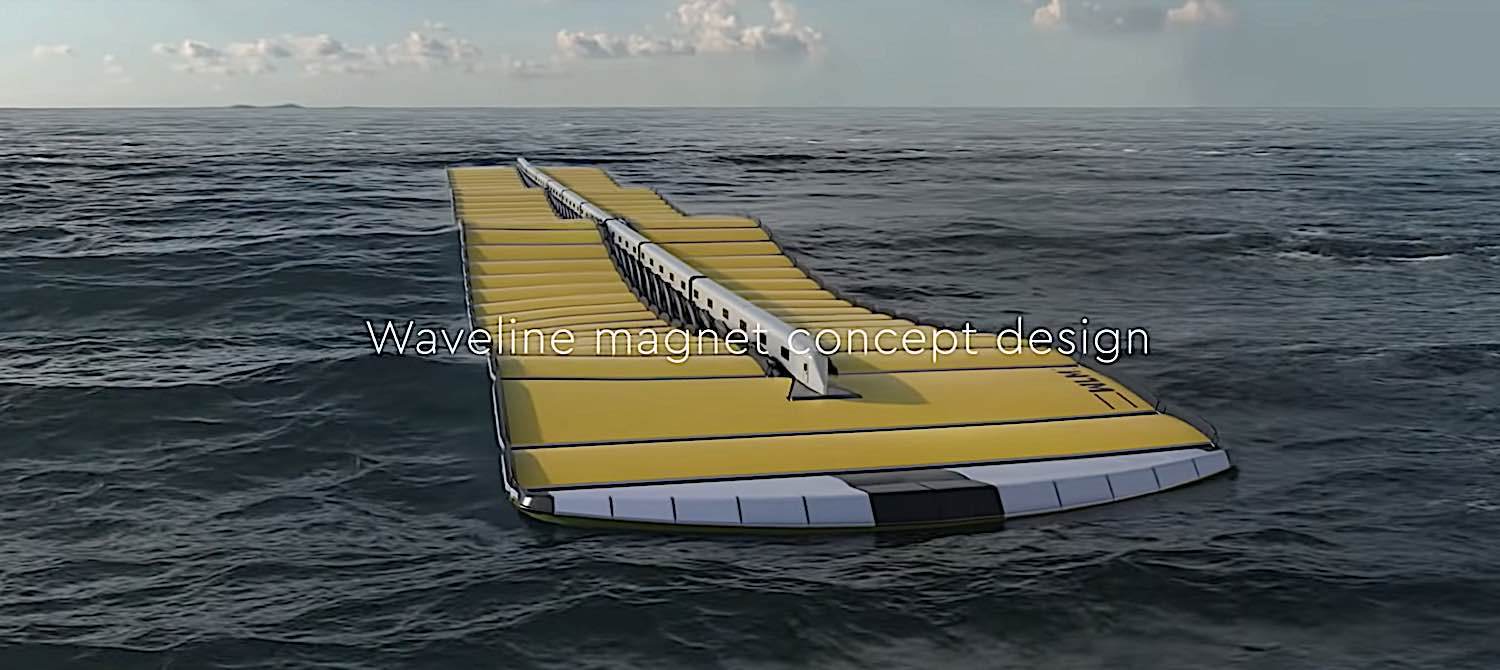

The Waveline Magnet
After working on technology to harness the energy of ocean waves for over a decade, Cyprus-based company Sea Wave Energy Limited (SWEL) has designed a floating device that they believe can revolutionize wave energy generation.
The prototype, called the Waveline Magnet, is made up of a series of floating platforms connected by what looks like a spine. [3]
The design is flexible to allow the device to move up and down with the waves and follow their movement. This design enables the device to control how much energy is extracted from the wave in a controlled manner.
The manufacturer claims that the device can generate up to 100 MW of electricity under the right conditions. And paired with a low cost of production, the device could be a game-changer in the wave energy market.
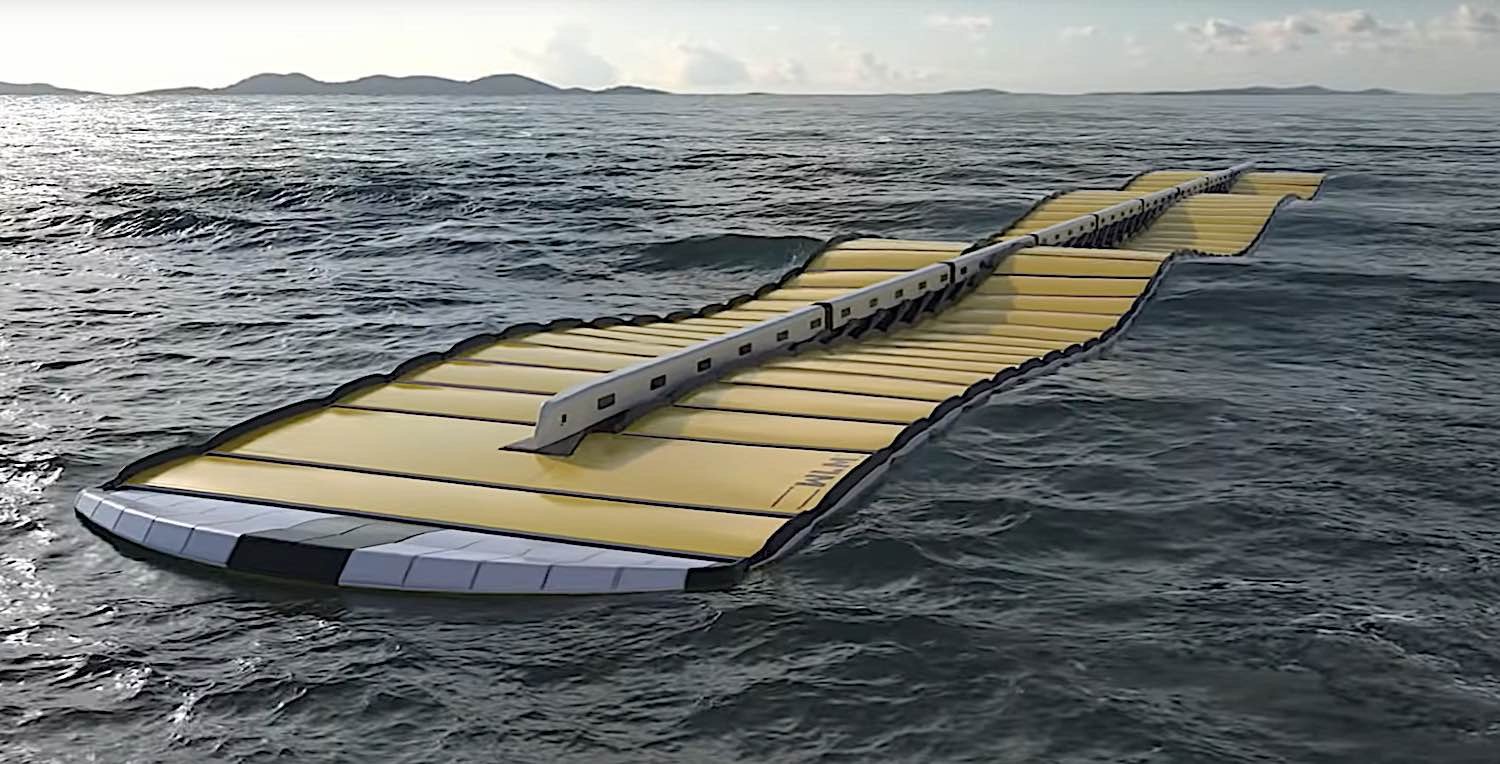

Manufacturing the Waveline Magnet
One of the most significant advantages of this technology is how easy and low-cost it is to manufacture.
Here are some of the advantages that the Waveline Magnet brings to the market:
- It can be manufactured using recycled materials, adding to the sustainability credentials of the project.
- It does not require specialized production lines or significant infrastructure, meaning it can be produced in any country with a relatively low level of industrial development.
- The prototype has a low mass of materials used per square meter, which helps to keep the manufacturing costs low.
- Thanks to the simplicity of the design and the manufacturing process, the Waveline Magnet can be mass-produced and deployed in very little time (in weeks rather than months).
- The modular and lightweight design means that the costs of deploying the device and retrieving it when needed are also very low.
- Thanks to the simple, modular design, maintenance, and repair costs are also very low.
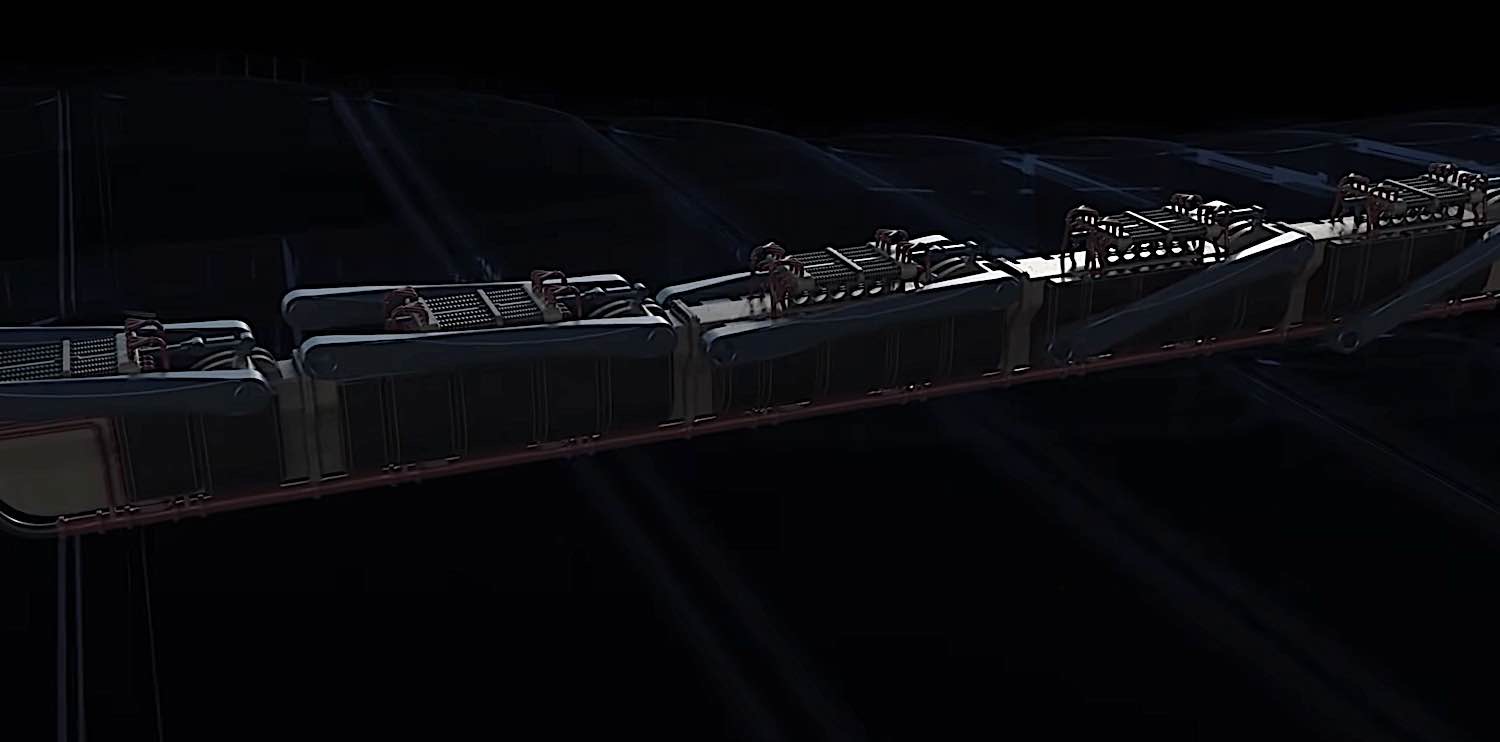

Because of the spine-like mobility of this WEC, the company is confident that it will be able to move with the waves instead of opposing them, no matter the conditions. This means that it is expected to survive in the often treacherous ocean conditions without any trouble.
With its many advantages and potential for low-cost mass production, the Waveline Magnet could be a game-changer in the wave energy market.
Commercializing the Wave Magnet
This WEC has the characteristics needed to succeed in the commercial market.
So far, it has been tested both in the controlled conditions of wave tanks and in a real-life sea environment in Larnaca Bay in Cyprus.
Further testing is needed to optimize the design and prove its long-term performance, but the potential is there.
The Waveline Magnet could avoid many of the pitfalls that other alternative energy sources have faced, such as the high initial investment and land usage for solar and wind farms or the sustainability issues from using rare-earth minerals in electric vehicles or solar panels.
And thanks to its low cost of production and easy manufacturing process, the use of the Waveline Magnet could quickly spread, making it the world’s most efficient and widely used wave energy generator.
What is wave energy?
Wave energy is a type of renewable energy that converts the energy from ocean waves into electricity. It is a relatively new technology with great potential, as the oceans are a never-ending energy source.
Wave energy has many potential benefits over other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power. Some of these advantages include the following:
- It is abundant. There is a lot of potential for wave energy due to the vast amount of coastline worldwide.
- It is consistent. Unlike solar and wind power, which are intermittent, wave energy is more predictable and can provide a steadier source of electricity.
- It has a low environmental impact. Wave energy does not produce any greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
- It is efficient. Wave energy can be converted into electricity quite cheaply and with very little energy loss in the process.
Despite these advantages, wave energy is still in the early stages of development and has not yet been commercialized on a large scale.
How does wave energy work?
In order to tap into the energy of waves, special devices called wave energy converters (WECs) are used.
There are many different types of WECs, but they all work by using the up-and-down motion of waves to drive a generator that produces electricity.
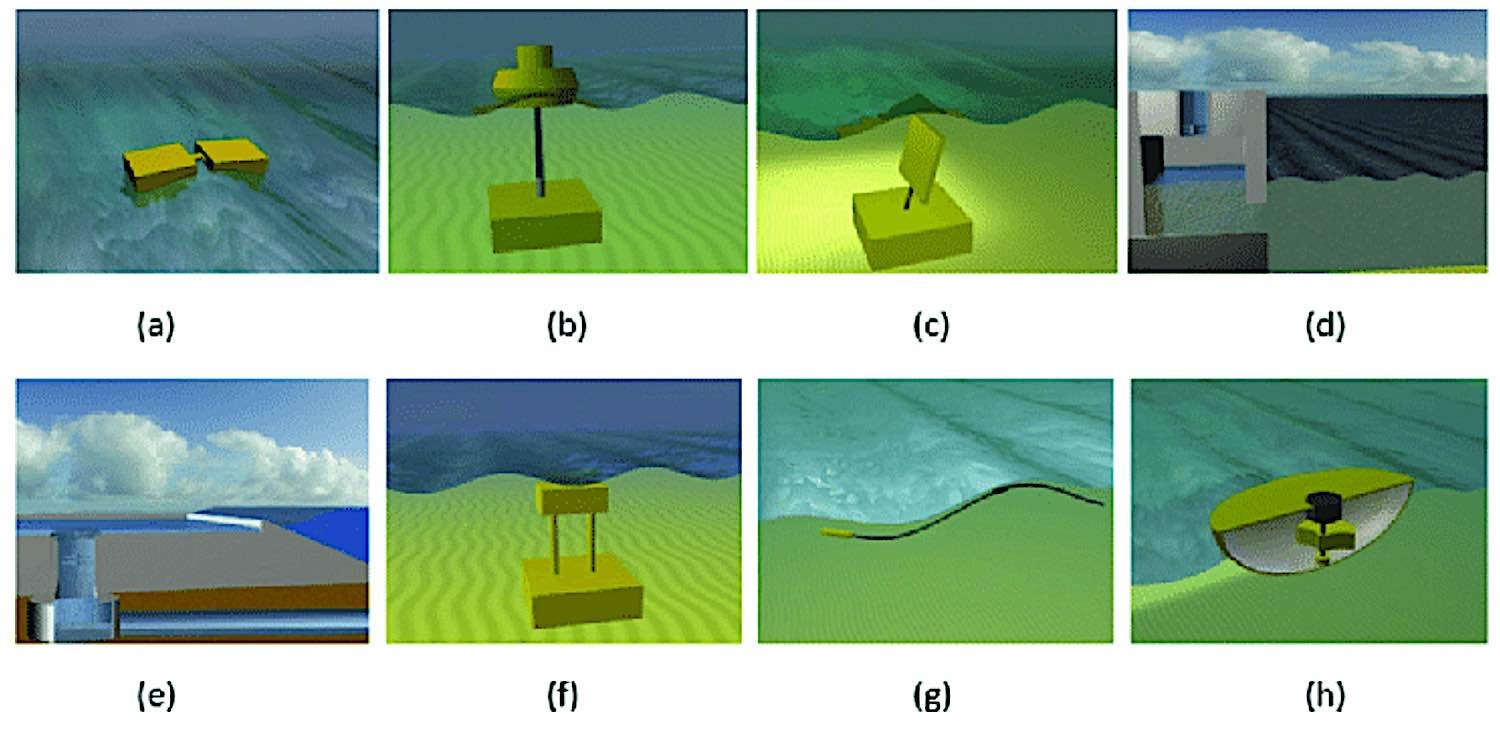
Here are a few types of WECs used to generate wave energy: [1]
- Point absorbers are devices that are anchored to the seafloor and move up and down with the waves. They convert the kinetic energy of the waves into electrical energy through a generator.
- Attenuators are floating devices placed perpendicular to the waves that capture the energy from the wave crests by moving back and forth. They also convert the kinetic energy of the waves into electrical energy but do so through hydraulic pumps that drive a generator.
- Oscillating Water Column (OWC) devices are anchored to the seafloor and have a chamber that is open to the ocean. As waves pass through the capture chamber, they cause the water level to rise and fall, compressing the air inside the room, which in turn drives a turbine that produces electricity.
- Overtopping is a method by which waves are diverted into a reservoir where they drive a turbine connected to a generator, similar to a hydropower dam.
- Inverted-Pendulum devices use the device’s weight to stabilize it against the waves while a paddle attached to the device moves back and forth, driving hydraulic pumps that, in turn, operate a generator.
Each of these devices has its own advantages and disadvantages. Point absorbers are typically more efficient than attenuators but are also more expensive to build. OWC devices are less expensive, but their efficiency is lower.

Regardless of design, there hasn’t been any large-scale commercialization of any type of wave energy converter yet. Although there have been many pilot projects and small-scale commercial installations, the technology is still in its infancy and hasn’t been scaled up to meet the needs of a large population.
However, a unique spine-like floating device designed by a startup based in Cyprus promises to harness the energy of the waves and convert it into electricity — more cost effectively [2]
What alternative energy sources do we have today?
The world is still largely dependent on fossil fuels for its energy needs. However, with the ever-growing concerns about climate change and air pollution, there is a greater focus on finding sustainable and renewable energy sources.
Here are some of the most popular alternative energy sources that are being explored today:
- Solar energy. Solar energy is one of the most popular renewable energy sources today. It can be used to generate electricity or heat, and it is also becoming increasingly popular for use in solar-powered cars and homes. The problem with solar energy is that it is not always available, as it depends on when the sun is out.
- Wind energy. Wind energy is another one that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It can be used to generate electricity or to pump water. The main disadvantage of wind energy is that it is not always reliable, as the wind doesn’t always blow.
- Hydro energy. Hydro energy is a renewable energy source that uses water to generate electricity. Hydro energy is usually harnessed through dams and can be used to irrigate land as well. The main disadvantage of hydro energy is that it can cause environmental problems, such as the displacement of people and the flooding of the land. It also requires a large amount of water to be available, which is not always the case in many regions or in times of drought.
- Hydrogen: Hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe. It can be used as fuel for cars, trucks, and buses, and also to generate electricity. The main disadvantage of hydrogen is that it is actually manufactured using electricity in the process, so it is only as clean as the source of that electricity.
- Geothermal: Geothermal energy comes from the heat of the earth’s molten core. It can be used to generate electricity or to heat and cool buildings. It is already used in countries like Iceland or the US. The disadvantage is that it can only be harnessed in certain areas with significant geothermal activity.
All alternative energy sources have their advantages and disadvantages.
The key is to find the right mix of energy sources that will work for a particular region or country and to carry on researching how to tap into these energy sources more efficiently.
Sources
[1]: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Types-of-WECs-a-attenuator-b-point-absorber-c-oscillating-wave-surge-converter-d_fig1_324999559
[2]: https://interestingengineering.com/innovation/floating-device-generate-power-waves
[3]: https://swel.eu/#more

































