There is a new innovative technology that may finally be able to remove up to 99.99% of salt from seawater and provide millions of people around the world with access to drinkable water that may also be used for irrigation and much more.[1]
Although desalinating saltwater has been possible for some time and has received a lot of funding from institutions around the world, problems regarding the cost and efficiency of different desalination techniques have for a long time prevented the world’s oceans from being used as a source of freshwater.

That is until a team of Korean scientists from the Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology developed a nanofiber membrane with unique hydrophobic qualities that are absolutely essential for the membrane distillation process.
This comes as welcome news as unpredictable global weather patterns have led to much drier than normal climates in many parts of the world, including the US.[2] For some perspective, approximately 71% of the planet’s surface is covered in water, from oceans to lakes and glaciers. But out of all of the water on the planet, only 3% is fresh water and only a small 0.5% is available as accessible freshwater.[3] The rest of the world’s freshwater is currently locked up in glaciers, ice caps, and in the atmosphere and soil.

When it comes to membrane distillation, one of the issues that researchers have struggled with in the past is the fact that in order for distillation to work, the membrane itself needs to stay dry. This is because when the membrane is dry, it can prevent liquid water molecules from moving through the membrane while permitting water vapor.
This way, when saltwater is heated, the water vapor can pass through the membrane and condense on the other side, leaving everything that doesn’t evaporate, such as salt, behind.
When the membrane becomes wet and is saturated, liquid water along with all of the contained salt, can readily pass through and defeat the entire filtration process. Previously when this happened, the membrane would need to be replaced frequently, halting the entire process and severely restricting the feasible filtration speed.
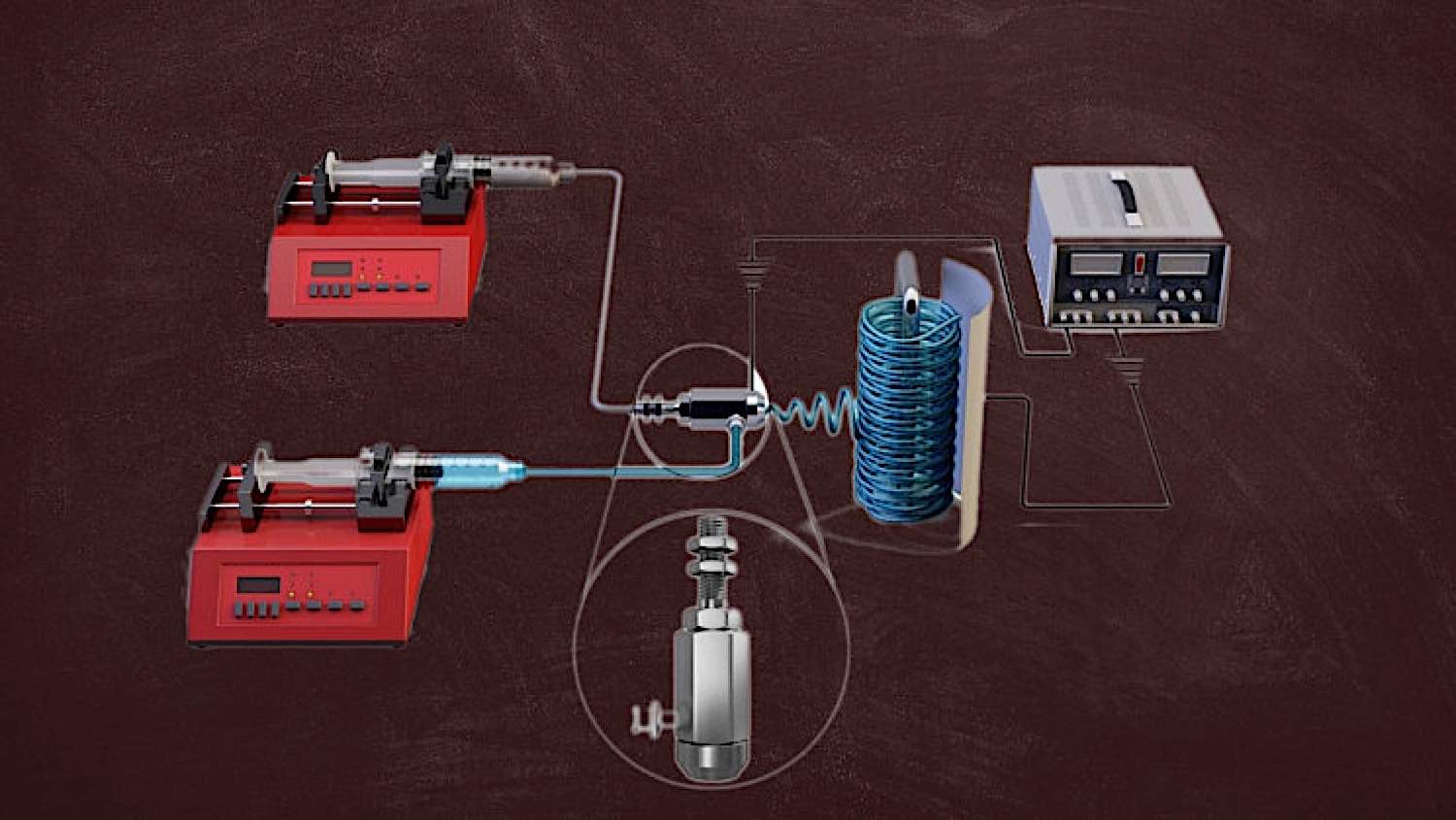
The Korean team of researchers tested their nanofiber membrane for a continuous 30-day trial, and at the end of the 30 days, it was discovered that their membrane was still able to filter 99.99% of salt from water, indicating that they had developed a revolutionary and innovative technology that has the potential to solve many of the world’s water issues.
The stable performance electrospun nanofiber membrane consists of a poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) core, with a silicone aerogel combined with a polymer to create the covering. Nanofibers are then arranged in a 3D hierarchical structure, creating an extremely hydrophobic material that resists moisture. Previous electrospun nanofibers only functioned on average for 50 hours when used in membrane distillation, indicating just how revolutionary this technological innovation is.
NOTES
[1] Science Direct, “Co-axially electrospun superhydrophobic nanofiber membranes with 3D-hierarchically structured surface for desalination by long-term membrane distillationn” April 1, 2021.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0376738820316008?via%3Dihub
[2] NPR, “The Drought In The Western U.S. Is Getting Bad. Climate Change Is Making It Worse,” June 9, 2021. https://www.npr.org/2021/06/09/1003424717/the-drought-in-the-western-u-s-is-getting-bad-climate-change-is-making-it-worse#:~:text=Climate%20Change%20Is%20Making%20It%20Worse,-Listen%C2%B7%204%3A25&text=Sullivan%2FGetty%20Images-,Warmer%20temperatures%20are%20leading%20to%20emptier%20reservoirs%20across%20the%20West,Lake%20Oroville%20in%20Northern%20California.&text=By%20almost%20every%20measure%2C%20the,one%20for%20the%20record%20books
[3] USBR, “Water Facts – Worldwide Water Supply”, November 4, 2020.